1. What are Wildfire Events?
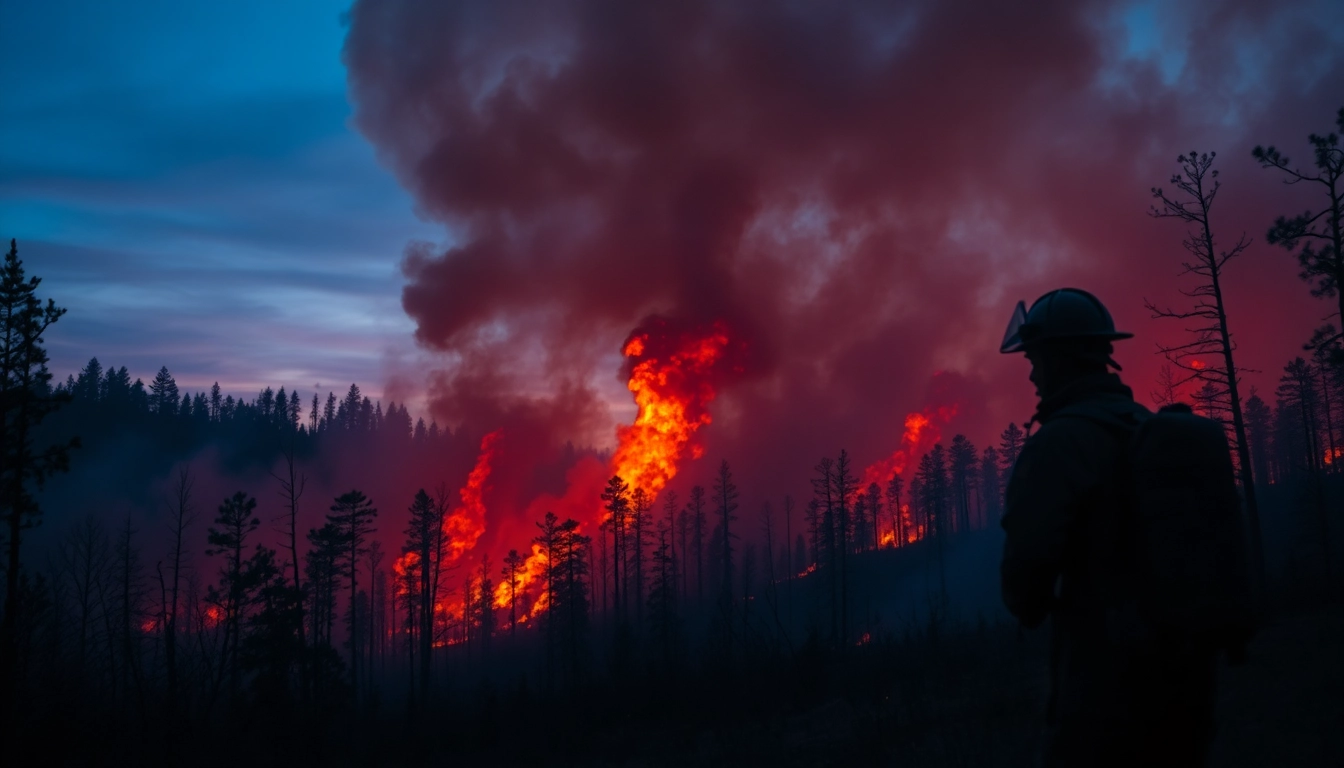
Wildfire events are uncontrolled fires that spread through vegetative areas, often fueled by dry conditions, wind, and expansive amounts of fuel, such as trees and underbrush. These incidents can lead to devastating impacts on both human settlements and natural ecosystems. Understanding the multi-faceted nature of Wildfire events is crucial for effective management and prevention strategies.
1.1 Definition and Types
Wildfire events, commonly referred to as forest fires, brush fires, or grass fires, can be classified based on several criteria:
- Type: Wildfires can be categorized into different types, such as surface fires, ground fires, and crown fires, each representing how fire travels through a particular layer of vegetation.
- Causes: Wildfires can ignite due to natural causes, such as lightning strikes or human activities, including campfires, smoking, arson, or sparks from machinery.
- Scale: Size and intensity can vary significantly, from small spot fires contained easily to large, uncontained infernos that can last for weeks or months.
1.2 Common Causes of Wildfires
Understanding the root causes of wildfire events is essential for prevention. Major causes include:
- Human Activity: Campfires left unattended, discarded cigarettes, and arson are leading causes of wildfires.
- Natural Events: Lightning strikes often ignite wildfires, especially during dry seasons.
- Climate Change: Increased temperatures and prolonged drought conditions exacerbate wildfire risks.
1.3 Environmental Impact of Wildfire Events
The ramifications of wildfire events extend well beyond immediate damage. Key impacts include:
- Loss of Biodiversity: Wildfires can lead to habitat destruction, displacing wildlife and reducing biodiversity.
- Soil Erosion: Without vegetation, soil can erode more easily, leading to land degradation.
- Air Quality Issues: Smoke from wildfires can significantly affect air quality, leading to health concerns for nearby populations.
2. The Science Behind Wildfire Events
2.1 Weather Conditions Favoring Wildfires
Specific weather patterns can significantly influence wildfire likelihood and intensity. Factors include:
- Temperature: High temperatures can create ideal conditions for wildfires, drying out vegetation.
- Humidity: Low humidity levels enhance fire spread, as dry air contributes to desiccating fuels.
- Wind: Strong winds can carry flames to new areas, exacerbating wildfire risks and complicating firefighting efforts.
2.2 Fire Behavior and Dynamics
The dynamics of fire behavior are influenced by several factors, including fuel type, moisture content, and topography. Understanding these behaviors is essential for effective management:
- Flame Propagation: The rate at which fire spreads varies significantly based on fuel and weather conditions.
- Heat Release: The amount of heat produced during combustion affects both the fire’s intensity and the ecosystem’s recovery potential.
2.3 Role of Vegetation in Wildfire Events
Vegetation type and density can either contribute to or help mitigate wildfire risk. Key points include:
- Fuel Load: Areas with high fuel loads are more susceptible to intense wildfires.
- Vegetative Variety: Diverse ecosystems may recover more robustly from wildfires while providing natural firebreaks.
3. Preparing for Wildfire Events
3.1 Essential Prevention Measures
Preparation and prevention are key in minimizing the impact of wildfire events. Effective measures include:
- Creating Firebreaks: Establishing firebreaks can help to slow or stop the spread of fire.
- Regular Maintenance: Clearing debris and maintaining landscapes can dramatically reduce fire risks.
- Community Engagement: Engaging community members in wildfire preparedness efforts fosters collective responsibility.
3.2 Community Awareness and Education
Educating communities about wildfire risks and response strategies is crucial. Key strategies include:
- Workshops and Training: Offering educational workshops can empower individuals to act during wildfire events.
- Information Dissemination: Utilizing multiple channels (online, local media) ensures broad access to information.
3.3 Creating Wildfire Defensible Space
Defensible space around properties can significantly limit fire spread. Consider the following tips:
- Zone Management: Create buffer zones with clear vegetation management practices at various distances from your home.
- Building Materials: Using fire-resistant materials in construction can reduce vulnerability to wildfires.
4. Responding to Wildfire Events
4.1 Emergency Response Strategies
Effective emergency response is vital during wildfire events. Strategies include:
- Evacuation Plans: Local authorities should implement evacuation plans that can be activated quickly.
- Communication Systems: Ensuring that robust communication systems are in place promotes quicker response times.
4.2 Firefighting Techniques and Tools
Firefighters utilize various techniques and tools in combating wildfires. Key tools and techniques include:
- Ground Crews: Firefighters on the ground use hand tools to create containment lines.
- Aerial Support: Helicopters and airplanes can drop water or retardants to suppress fire spread.
4.3 Evacuation and Safety Protocols
Ensuring community safety during wildfires involves stringent evacuation protocols. Effective approaches include:
- Early Warning Systems: Use alert systems to provide early warnings for residents.
- Clear Routes: Identify and maintain evacuation routes to ensure accessibility during emergencies.
5. Recovering from Wildfire Events
5.1 Ecological Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery after wildfire events is essential for ecosystem restoration. It includes:
- Soil Rehabilitation: Implementing erosion control measures post-fire helps in soil recovery.
- Planting Native Species: Replanting with local flora can aid in natural recovery.
5.2 Supporting Affected Communities
Communities recovering from wildfire events require substantial support. Effective recovery strategies include:
- Financial Assistance: Providing funding for affected residents can help in rebuilding efforts.
- Community Programs: Establishing community programs can foster resilience and emotional support among residents.
5.3 Long-term Solutions and Policies
Effective long-term solutions and policies to mitigate wildfire impacts include:
- Land Management Policies: Implementing strategic land management can help reduce susceptibility to wildfires.
- Investment in Research: Funding research on wildfire behavior enhances prevention and response methodologies.
FAQs About Wildfire Events
What is the most famous wildfire in history?
The Peshtigo Fire, occurring in Wisconsin, is the deadliest wildfires in history, claiming over 1,500 lives.
What is a wildfire event?
A wildfire event is an uncontrolled fire that occurs in undeveloped land. It can be caused by natural processes or human activities.
How can we prevent wildfires?
Preventative measures include proper land management, public education, and creating defensible space around properties.
What should I do during a wildfire evacuation?
Follow local authorities’ evacuation orders, take essential belongings, and use pre-planned evacuation routes.
How do wildfires impact air quality?
Wildfires release large amounts of smoke and particulate matter, which can significantly degrade air quality and harm health.